In industrial environments, fans are rarely “background equipment.” They run for long hours, often continuously, and quietly contribute to a significant portion of a facility’s energy consumption. For decades, induction motor fans have been the default choice. Today, however, industries are increasingly re-evaluating that choice.
The comparison between BLDC fans and conventional induction fans is no longer theoretical. It is driven by real operating data, rising electricity costs, and the need for reliable, long-term efficiency. When power consumption is examined over actual industrial operating hours, the difference becomes difficult to ignore.
Understanding Power Consumption in Industrial Fans
Induction fans consume high power primarily because of how the motor converts electrical energy into mechanical output. A large portion of energy is lost as heat, especially during continuous operation. In industrial settings—factories, warehouses, substations, and processing plants—fans often run 12 to 24 hours a day. Over time, this inefficiency translates into substantial energy wastage.
BLDC (Brushless Direct Current) fans operate on a fundamentally different principle. Electronic commutation replaces mechanical losses, allowing more electrical input to be converted directly into airflow rather than heat. The result is significantly lower power consumption for the same air delivery.
BLDC vs Induction: The Real Power Difference
In industrial applications, induction fans typically consume two to three times more power than BLDC fans delivering comparable airflow. While switching a fan off reduces usage hours, it does not address the core inefficiency of the motor itself.
BLDC fans consume less power every single minute they operate. Over thousands of operating hours annually, this difference compounds into measurable energy savings, lower electricity bills, and reduced load on electrical infrastructure.
Why Power Efficiency Matters Beyond Cost
Power consumption is not just about cost savings. Higher energy draw means higher heat generation inside the motor, which impacts reliability and lifespan. Induction fans running continuously tend to experience faster wear, increased maintenance needs, and higher downtime.
BLDC fans generate significantly less internal heat. This results in more stable performance, longer service life, and reduced maintenance intervention—critical advantages in industrial environments where downtime is expensive.
Operational Stability Under Industrial Conditions
Industrial power conditions are rarely perfect. Voltage fluctuations, dust, and high ambient temperatures are common. Induction fans are sensitive to these conditions, often showing speed variation and increased power draw.
BLDC fans, by contrast, are designed to maintain stable performance even under fluctuating voltage. This consistency ensures predictable airflow and controlled power consumption, improving overall operational stability.
Airzon’s BLDC Advantage for Industrial Applications
Airzon’s BLDC industrial fans are not adaptations of residential products. They are engineered specifically for industrial duty cycles and harsh environments.
Key advantages of Airzon BLDC fans include energy-efficient motors optimized for continuous operation, all-metal construction with no plastic components, and significantly lower power consumption compared to conventional induction fans. Reduced internal heat means lower risk of coil failure, improved safety, and longer equipment life.
Airzon’s design philosophy focuses on practical efficiency—delivering strong airflow with minimal energy input while ensuring reliability across long operating hours.
Long-Term Impact of Switching to BLDC Fans
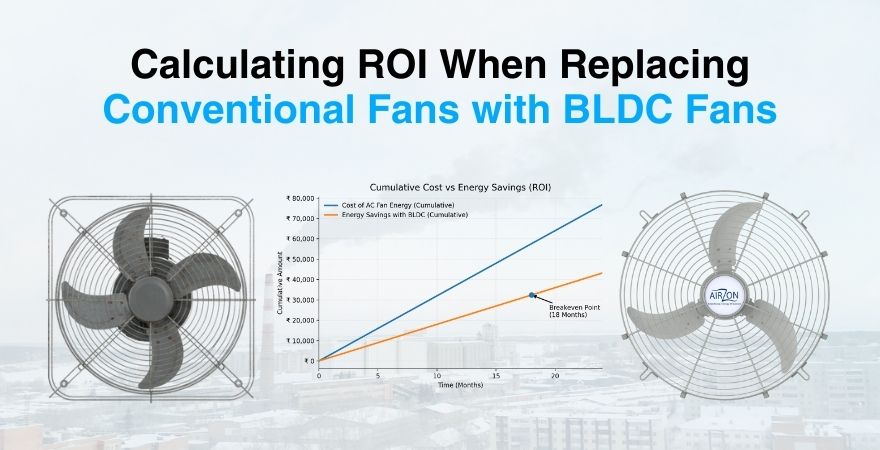
When industries compare BLDC and induction fans over a single day, the difference may seem modest. When compared over a year, the impact becomes substantial. Lower electricity consumption, reduced maintenance, improved uptime, and longer service life collectively deliver a strong return on investment.
More importantly, switching to BLDC technology aligns industrial operations with modern energy-efficiency goals without compromising performance.
Conclusion
The comparison between BLDC and induction fans for industrial use is no longer about preference—it is about efficiency, reliability, and long-term value. BLDC fans consistently demonstrate lower power consumption, improved operational stability, and reduced lifecycle costs.
With purpose-engineered BLDC solutions, Airzon enables industries to move beyond outdated induction technology and adopt airflow systems that are efficient, durable, and built for continuous operation. In today’s energy-conscious industrial landscape, BLDC fans are not the future—they are the smarter standard.